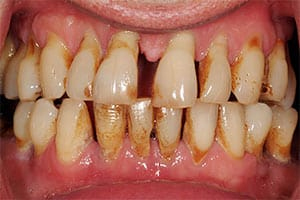
Gum Disease
We at Stoma Advance Dental Care believe that teeth are for life. Gum care is of prime importance to us because gum disease is a major cause of tooth loss in adults as this is an infection of the tissues that surround and support teeth.
Gingivitis
Gingivitis, the earliest stage of gum disease, is inflammation of the tissues surrounding and supporting the teeth and is most commonly a result of poor dental hygiene or plaque, the sticky color less bio-film of bacteria that adhere to teeth at and below the gum line. This bacteria produces toxins or poisons, which irritate the gums, causing them to turn red, swell or bleed. If not carefully removed by daily brushing and flossing, plaque hardens into a rough, porous substance know as calculus. This cannot be removed without professional cleaning. With prolonged irritation, the gums separate from the teeth, causing pockets (spaces) to form. Gingivitis is a very common condition and varies widely in severity. It is characterized by red, swollen gums that bleed easily when teeth are brushed or flossed. Gingivitis is not the same thing as periodontitis. Gingivitis always precedes and acts as a warning sign for the more serious condition of periodontitis.
Periodontitis
Untreated gingivitis can advance to periodontitis. With time, plaque can spread and grow below the gum line and the tissues and bone that support the teeth are broken down and destroyed. If left untreated, this leads to tooth loss. Periodontitis can be aggressive or chronic. Aggressive Periodontitis occurs in patients who are otherwise clinically healthy. Common features include rapid attachment loss and bone destruction and familial aggregation. While Chronic Periodontitis results in inflammation within the supporting tissues of the teeth, progressive attachment and bone loss and is characterized by pocket formation and/or recession of the gingiva.
Factors Affecting the Health of your Gums
Periodontal Diseases and Tobacco:Current studies link periodontal disease with tobacco usage. There is a greater incidence of calculus formation on teeth, deeper pockets between gums and teeth as well as greater loss of the bone and fibers that hold teeth in your mouth. Chemicals in tobacco such as nicotine and tar, slow down healing and the predictability of success following periodontal treatment.
Diabetes and Oral Health: Individuals suffering from diabetes, especially uncontrolled diabetics, have a higher risk of developing bacterial infections of the mouth. These infections impair your ability to process insulin, resulting in greater difficulty with controlling your diabetes. Inform the dentist about your history and the current status of your condition.
Women and Periodontal Health: Hormonal changes during puberty, pregnancy and menopause affect many of the tissues in your body, including your gums. Your gums become sensitive, and more susceptible to gum disease. During puberty, there is increased production of sex hormones. These higher levels increase gum sensitivity and lead to greater irritations from plaque and food particles. The gums can become swollen, turn red and feel tender. Similar symptoms appear several days before menstruation. There can be bleeding of the gums, bright red swelling between the teeth and gum, or sores on the inside of the cheek. The symptoms clear up once the period has started. As the amount of sex hormones decrease, so do these problems.
Between the second and eighth month during pregnancy, gums swell, bleed and become red or tender. Periodontal health should be part of your prenatal care. Any infections during pregnancy, including periodontal infections, can place a baby’s health at risk. Swelling, bleeding and tenderness of the gums may also occur when you are taking oral contraceptives, which are synthetic hormones. Changes in the look and feel of your mouth also occur during menopausal or post- menopausal period of life. These include feeling pain and burning in your gum tissue and salty, peppery or sour tastes. Careful oral hygiene at home and professional cleaning may relieve these symptoms.
Stress is also is a risk factor for periodontal disease.
Medications, such as oral contraceptives, anti-depressants, and certain heart medicines, can affect your oral health. Inform your dentist if you are on these.
Clenching or Grinding Your Teeth at night in sleep can put excess force on the supporting tissues of the teeth and could speed up the rate at which these periodontal tissues are destroyed.
A diet low in important nutrients can compromise the body's immune system and make it harder for the body to fight off infection.
Other Systemic Diseases that interfere with the body's immune system may worsen the condition of the gums. Ongoing research shows that periodontal disease may be linked to Heart Disease, Diabetes, Respiratory Disease or Osteoporosis. The bacteria associated with periodontal disease can travel into the blood stream and pose a threat to other parts of the body.'
Be cautious if a family member has Periodontal Disease because the bacteria causing periodontal disease can pass through saliva, putting children at risk for contracting the periodontal disease from another family member.
Treatment at Stoma Advance Dental Care
Visit us if you have gums that bleed easily; red, swollen or tender gums; gums pulled away from the teeth; persistent bad breath; pus between the teeth and gums; loose or separating teeth and a change in the bite. We will detect your periodontal disease through a periodontal evaluation. Stoma Advance Dental Care offers both non- surgical periodontal treatment and surgical treatments.
Non-surgical treatment Non-surgical treatment is suggested for mild forms of periodontitis. These involve scaling and root planning followed by adjunctive therapy such as systemic antibiotics and local delivery of antimicrobials, as needed on a case-by-case basis. Scaling and Root Planing is removal of plaque and calculus (tartar) deposits beneath the gum line. The tooth roots may be cleaned allowing the gum tissue to heal and reattach to the tooth. In some cases, the occlusion (bite) may require adjustment. Systemic Antibiotics or irrigation with anti-microbials (chemical agents or mouth rinses) is also given to patients to control the growth of bacteria that create toxins and cause periodontitis. In some cases, laser may be used to remove diseased tissue in the gum pocket, eliminate bacteria and stimulate healing cells.
Periodontal surgery is necessary when tissues around your teeth are unhealthy and cannot be repaired with non-surgical treatment. Following are the four types of surgical treatments prescribed for patients:
During Pocket Reduction Procedures the gum tissue is folded back and disease causing bacteria is removed before securing the tissue into place.
Guided Tissue Regeneration is recommended when the bone supporting your teeth has been destroyed. During this procedure, the gum tissue is folded back and disease- causing bacteria is removed. Membranes (filters), bone grafts and/or tissue- stimulating proteins are used to encourage body's natural ability to regenerate bone and tissue.
Crown Lengthening is required when the tooth needs a new crown or other restoration. During this procedure, excess gum and bone tissue is reshaped to expose more of your natural teeth, which can significantly enhance periodontal health. Crown Lengthening procedure can be effectively done with lasers.
During Soft Tissue Grafts gum tissue is taken from the palate or another donor source to cover the exposed root. The graft is then gently adapted and sutured into the recipient site to either cover exposed root surfaces and/or to create a wide band of protective gum tissue. This can be done for one tooth or several teeth to even your gum line and reduce sensitivity.This may reduce tooth sensitivity and improve esthetics of your smile
Patients Role & Follow Up Visits
The first responsibility is to eliminate factors that increase susceptibility to periodontal disease, these include smoking, diabetes and excessive use of alcohol. Secondly, it is important to maintain plaque control. This is achieved through brushing and using other home care aids such as floss, interdental brushes and rubber tips. Lastly, you are responsible for scheduling regular periodontal maintenance. Most patients with moderate to advanced cases or patients should have periodontal maintenance appointments every three to four months for their lifetime.
Recall
Recall appointments are of great importance after any treatment. It is important to check for healing of tissues, alteration in the patient’s suggested habits and their willingness to maintain their oral hygiene.