Dental Care during pregnancy
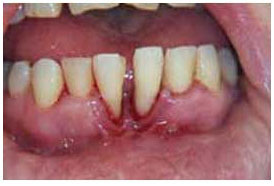
Pregnant women tend to have oral health problems due to hormonal changes. At Stoma Advance Dental Care, we give due precaution both for mother and child. Aggressive treatments are postponed for post delivery. During pregnancy gum tissue swells, become inflamed, bleed and is often painful and sensitive. These reactions are due to the plaque surrounding the teeth. Between the second and eighth month, gums may swell, bleed and become red or tender. Large lumps may appear as a reaction to local irritants. However, these growths may require professional removal, but usually disappear after pregnancy. Any infections during pregnancy, including periodontal infections, can place a baby’s health at risk.
We advise
Pregnant women should have three or at least two dental cleanings during pregnancy. Practice good oral hygiene: Brush twice a day, for at least two minutes each time. Floss every day. Use an antimicrobial mouth rinse to help you control gum infection.
Maternity Dental Care
Pregnant women tend to have oral health problems due to hormonal changes. At Stoma, we give oral health care with due precaution both for mother and child. Aggressive treatments are postponed for post delivery. Pregnant women should have three or at least two dental cleanings during pregnancy. Home care should be excellent.
During pregnancy gum tissue swells, become inflamed, bleed and is often painful and sensitive. These reactions are due to the plaque surrounding the teeth. Between the second and eighth month, gums may swell, bleed and become red or tender. Large lumps may appear as a reaction to local irritants. However, these growths may require professional removal, but usually disappear after pregnancy. Any infections during pregnancy, including periodontal infections, can place a baby’s health at risk.
Oral Surgery and Pregnancy
The extractions are carried out in the 2nd trimester. Procedures to remove wisdom teeth are safe under local anaesthetic. In case of pain rinse your mouth with warm salt water 2 to 3 times a day. This will help reduce discomfort.
Pregnancy Gingivitis
Pregnancy gingivitis starts during second month of pregnancy due to increase in hormone levels. The level of progesterone in the body can be 10 times higher than normal. This enhances growth of certain bacteria that cause gingivitis. Immune system also works differently during pregnancy.
This could change the way your body reacts to the bacteria, that cause gingivitis. Gums look redder, swell and bleed when brushed. The condition peaks around the eighth month. It often tapers off after the baby is born. To minimize the effects of pregnancy gingivitis, practice good oral hygiene: Brush twice a day, for at least two minutes each time. Floss every day. Using an antimicrobial mouth rinse also may help you control your gum infection. .
Pregnancy Granuloma \ Pyogenic Granuloma \ Pregnancy Tumor)
Pregnancy granuloma are also known as a pyogenic granuloma or pregnancy tumor. These are not tumors nor are cancerous or even dangerous. They usually develop during second trimester, near upper gum line or elsewhere in the mouth, as red nodules. Pregnancy granulomas are attached to the gum or mucous membrane by a narrow stalk of tissue. They bleed easily and can form an ulcer or crust.
The exact cause of pregnancy granulomas is unknown, poor oral hygiene is a primary factor. Trauma, hormones, viruses and malformed blood vessels are suspected as co- factors. Women with these growths usually have pregnancy gingivitis. They disappear after your baby is born.
Your queries and our answers
How do I take care oral hygiene during pregnancy?
Eat a well-balanced, nutritious diet with plenty of protein, calcium and vitamins A, C and D. Brush your teeth twice a day for at least two minutes each time. Use fluoride toothpaste. Floss at least once a day. Use an antibacterial mouthwash to destroy bacteria that contribute to gingivitis.
Is it safe to visit the dentist during pregnancy?
The second trimester is the best time to receive routine dental care. If possible, avoid major procedures, reconstruction and surgery until after the baby is born.
Can I take emergency dental treatment while pregnant?
You should receive treatment to ease your pain, prevent infection or decrease stress. Consult with your obstetrician if there are questions about the safety of medicines or anesthesia.
Is it safe to get dental X-rays?
Dental X-rays are safe. A lead apron protects you and your fetus from radiation. Some dentists will put two lead aprons on a pregnant patient to make sure that the fetus is protected. However, most dentists do not recommend dental X-rays if you are pregnant or think you may be pregnant. X-rays usually are taken if they are needed for diagnosis or treatment that cannot wait until after the baby is born.
Can I take dental medications while pregnant?
Ideally, you should not take any medicines during pregnancy, especially during your first trimester. However, sometimes this is simply not possible because the benefits of a medicine outweigh the risks related to its use. Most common dental medicines can be used during pregnancy. However, sedatives and certain antibiotics should be avoided.
Can I take dental medications while nursing?
The amount of drug excreted into breast milk is usually small, about 1% to 2% of the dose taken. It is unlikely that dental medicines will affect your baby. You need to be more cautious about taking medicines if your baby is a newborn or premature and you are breastfeeding.
To minimize risk, medicines can be taken just after your baby has nursed. Then, try to avoid nursing for at least four hours or as long as you can. This will minimize the amount of drug that enters your breast milk. Most drugs reach their maximum concentration in milk one or two hours after you take them.